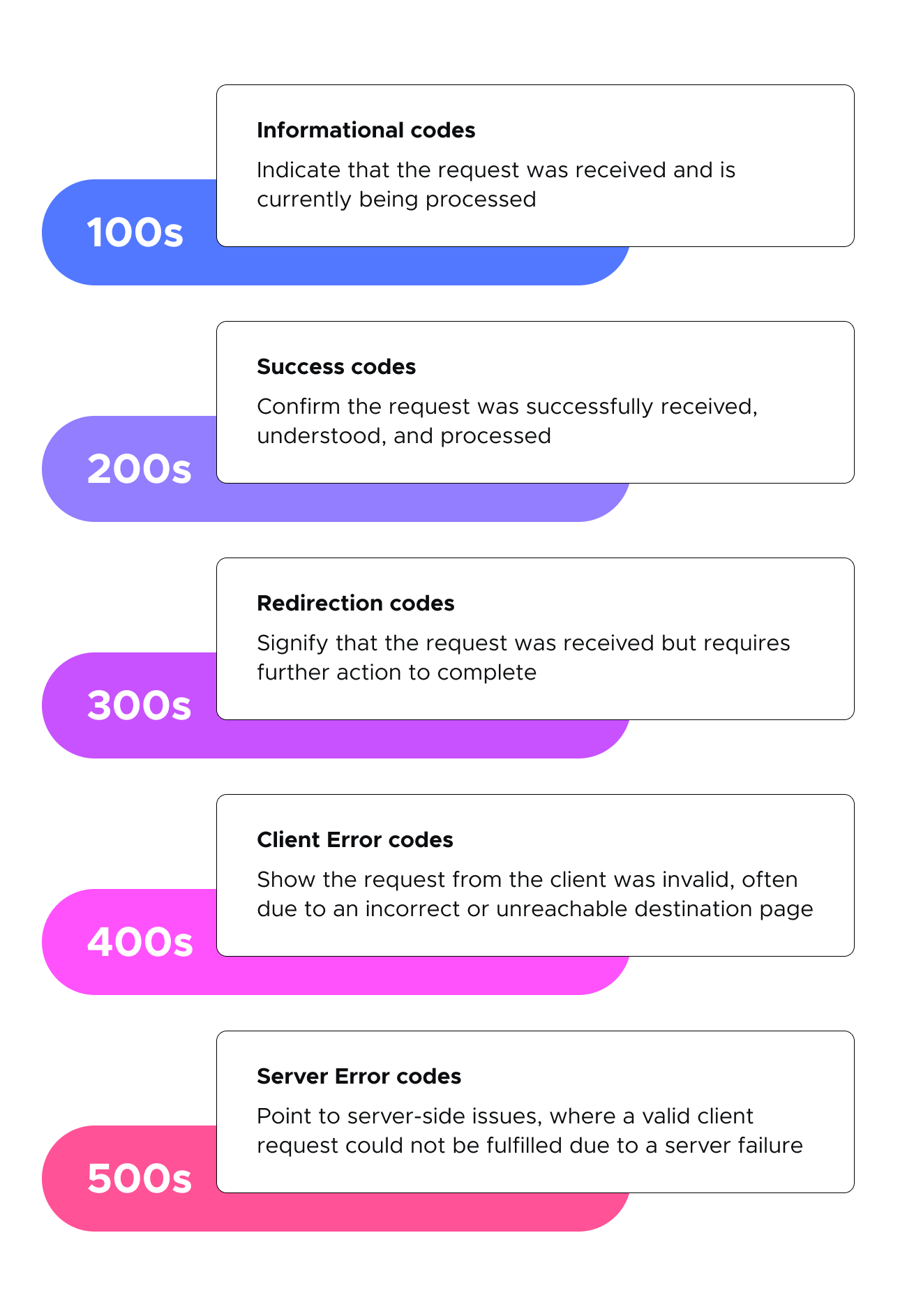
Meaning of different HTTP status codes
Status codes are represented by three numbers beginning with 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5. From 100s to 500s, HTTP response codes are divided into the following categories:
- 100s - Informational codes. The request was received and the operation is being processed.
- 200s - Success codes. The request was received and processed successfully.
- 300s - Redirection codes. The request was received but needs an additional step to complete.
- 400s - Client error codes. The request was made but the destination page is not correct.
- 500s - Server error codes. The request was made but the server failed to deliver the result.
Each HTTP status code has its subcategories.
Which response status codes impact my SEO negatively?
Codes from 300s to 500s hurt your website’s SEO. Let’s review the effect of these codes on search engine optimization in more detail.
301 moved permanently
This HTTP status code means that the requested page has been permanently moved to a new URL, requiring an extra step to reach the correct page. On your website, you should regularly review and update links to ensure they return a 200 (success) response. Too many redirects can slow down load times and hurt your SEO by making it harder for search engines to crawl your site efficiently.
302 found
A 302 status code means the server temporarily redirects a request to a different page while still expecting the original URL to be used for future requests. This approach isn’t ideal because it doesn’t clearly tell search engines that the page has permanently moved. As a result, search engines treat it as a temporary fix, which prevents link equity from being passed along and can negatively impact your SEO.
404 page not found
This HTTP status code indicates that the server didn’t find the requested URL. This issue might be temporary or permanent. For SEO, frequent 404 errors can hurt your website’s rankings, as they create a poor user experience and signal to search engines that your site isn’t well-maintained. Search engines might crawl your site less efficiently and view the affected pages as less valuable, which can hurt your site’s overall authority.
410 gone
410 status code indicated that the requested URL was permanently deleted from the server, with no new redirecting address. As 404 codes, 410 are bad for SEO because they create a dead end for both users and search engines.
503 service unavailable
A 503 status code means the server can’t handle a request right now, usually because it’s overloaded or the site is temporarily down for maintenance. This code is meant to let search engines know the issue is only temporary and they should come back later.
However, if a 503 status lasts too long or happens too often, it can be bad for SEO. Search engines might stop crawling your site as frequently, and visitors could get frustrated and leave, which can hurt your rankings over time.
Keep your website’s response status codes error-free with Drupfan
Don’t let errors in HTTP status codes drag down your SEO or frustrate users. Partner with Drupfan and we will make sure your site is running smoothly with only 200 response codes. From fixing broken links to optimizing on-page 300s redirects, we have you covered.