A custom Drupal theme gives us complete control over the look and feel of the interface. Unlike pre-built templates, a custom theme doesn’t contain unnecessary code that slows down the site. It adapts to specific design, branding, language needs, and accessibility requirements. This is crucial for optimal performance, security, future scalability, and long-term support. In addition, a custom theme completely avoids conflicts with third-party styles or unnecessary dependencies.
Getting Started with Drupal Theming: How to Create a Custom Theme

Drupal Theme System Basics: Understanding Theme Structure and Custom Drupal Theme Development
Drupal uses a powerful and flexible layered theming system based on Twig templates, PHP processors, and YAML configuration. Themes consist of HTML templates, styles, JavaScript, and pre-processing logic that allows you to define exactly how each page element is displayed.
File and Directory Structure
A standard theme includes the following key elements:
- .info.yml - theme description (title, base theme, regions)
- libraries.yml -styles, scripts, and binding dependencies
- templates/ Twig templates for pages, blocks, menus, nodes, etc.
- css/, js/, images/ custom styles, scripts, graphics
- theme-settings.php - custom theme settings (optional)
The file structure should be logical and clean for ease of maintenance and scalability.
Templates and Twig Overrides
Drupal uses Twig as its templating engine. This allows you to separate logic from markup. To customise the HTML structure, it is necessary to copy templates from the base theme (e.g. Classy) into your theme and modify them. Template names are formed based on the theme hook suggestions (e.g. node--article.html.twig). Additionally, you can use the preprocessing functions in the .theme file to prepare variables before rendering.
Resource Libraries
In Drupal theming, the libraries.yml file helps manage assets efficiently. Use it to group CSS and JS resources that can be attached to template files, components, or parts of your Drupal site. You can also define dependencies between libraries to prevent duplicate loading. For example:

This setup is essential when you create a custom theme. Drupal’s performance settings handle resource aggregation and minification, which helps keep your custom theme development clean and optimised. Avoid attaching unnecessary third-party styles to ensure faster loading times.
Accessibility and Responsive Design
A well-designed Drupal site adheres to accessibility standards (WCAG 2.1) and employs responsive design practices. During the development of the theme, use ARIA attributes, maintain proper heading structure, ensure color contrast, and support keyboard navigation. Responsive layouts are achieved using media queries in your CSS and mobile-friendly template files. These elements are key in any modern Drupal theming project.
Drupal Theme Development Checklist
Before launching, run through a checklist for your custom theme development. Check structure, code quality, accessibility, and performance. Ensure cross-browser compatibility and follow best practices in Drupal theming. This ensures your Drupal site looks great and functions well across all devices.
Check .info.yml and Clear the Cache
When getting started with Drupal theme development, make sure your .info.yml file is correctly structured. It should include valid fields like the theme name, base theme, regions, and libraries. This file defines your new theme and connects it to the rest of the system.
Even a small YAML error can cause issues with your Drupal core theme. After making changes, be careful and always clear the cache. Use the drush cr command or clear it through the admin interface. This activates any new styles, templates, or settings you've added while working on your Drupal project.
Check for Template Overrides
To create custom themes properly, ensure your Twig files are named correctly and placed in the right directories. Use Theme Debug (enabled in services.yml) to verify if the correct template is in use.
Avoid unnecessary duplication. Only override templates that truly need customisation. Keeping your theme structure clean improves maintainability and follows best practices for Drupal websites.
Test Styles on Mobile Devices and in Different Browsers
A custom Drupal theme must look consistent across all major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Test thoroughly.
Also, check mobile responsiveness. Use browser devtools or real devices. Test screen widths from 320px (phones) to over 1200px (desktops). This helps ensure the stability and usability of the theme for all users.
Check Accessibility (screen reader, keyboard navigation)
Accessibility is crucial, especially for users with disabilities. Every Drupal site should meet basic accessibility requirements. Confirm the following:
- All interactive elements are keyboard-accessible
- Headings follow a logical order (h1, h2, etc.)
- ARIA attributes are used properly
- The site works with screen readers like NVDA and VoiceOver
- Colour contrast is sufficient
These checks should be part of every custom Drupal theme workflow.
Resource Optimization CSS/JS Aggregation
Both core and custom themes benefit from CSS/JS aggregation. Drupal core provides settings for combining and minifying files, which helps reduce load times.
Go to /admin/config/development/performance to enable it. Clean up your theme structure by removing unused styles, especially those inherited from the base theme. This makes your Drupal websites load faster and use fewer resources.
When building modules and themes, attention to detail matters. Create a custom Drupal experience that’s fast, accessible, and well-structured. These checks help deliver a smoother experience for all users and set a solid foundation for your Drupal project.
Using View Modes and Correct Content Rendering
In theming in Drupal, always render content the right way. Use:
Use:
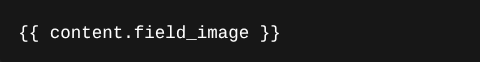
Instead of:
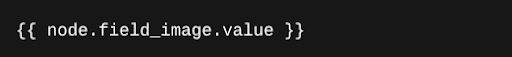
This method respects configuration options for formatting, security, and filtering. It also supports modules and structured rendering.
View modes like full, teaser, or custom let you create highly flexible layouts. They avoid code duplication and help make your theme compatible with various display needs.
No "Drupalisms" but clean templates, use contrib modules. Fences/No Markup
Avoid "Drupalisms", extra divs, spans, and messy HTML that slows down your web application. Clean templates are easier to maintain and improve both performance and SEO.
Use contrib modules like Fences or No Markup. They strip out unnecessary wrappers and make the markup lean. This makes it easier to style and improves search engine indexing.
Theme Development Best Practices for Drupal
Follow Drupal community best practices for cleaner, more maintainable themes. This helps ensure your theme is compatible with major updates and offers long-term support, which is important when building for clients or scaling large platforms.
Using base themes (Classy, Stable, Olivero, Barrio, Radix)
Start from a reliable base. Drupal development is faster with prebuilt themes like:
- Classy is structured HTML
- Stable is a minimalist layout
- Olivero is accessible and modern
- Barrio is Pattern Lab ready
- Radix is integrated with Bootstrap
Each base theme ensures solid configuration options and responsive behaviour across different devices.
Planning HTML5 structure and semantics
Use semantic HTML5: <article>, <section>, <nav>, <aside>. This supports accessibility and gives users an optimal viewing experience across devices.
Clean code means better UX, stronger SEO, and long-term sustainability.
Use Preprocess Hooks Instead of Editing Core Templates
While developing a custom theme in Drupal, don’t hardcode logic inside Twig templates. Use pre-process hooks in the .theme file instead. For example:
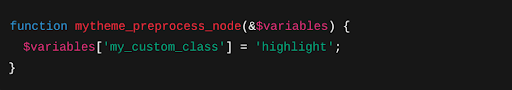
This separates logic from templates, making your custom theme in Drupal cleaner and easier to maintain. It’s a key step when creating a custom Drupal theme.
Test Drupal Updates and Compatibility with Changes in the Core
Always test your theme after core updates. Avoid editing core files or overriding classes in a parent theme. Use a child theme for performance to keep your customisations safe during upgrades. This is especially important in Drupal 9 themes and newer versions like Drupal 10 and 11. Updates in a staging environment ensure the theme across different platforms.
Optimise Loading: Critical CSS, Lazy Loading, Minification
Optimise Loading: Critical CSS, Lazy Loading, Minification
Improve performance by separating critical CSS into <head> and loading non-critical styles asynchronously. Use:
- Lazy loading for images (loading "lazy")
- Modern formats like WebP and SVG
- CSS/JS minification with tools like Webpack or Gulp
This ensures responsive design in Drupal themes and keeps your site fast.
Tools and Technologies in Drupal Frontend Development
Frontend Drupal development in 2025 is evolving fast. Modern tools make building themes quicker and more efficient. Creating a custom Drupal theme now involves utility-first CSS, flexible architecture, and smart workflows.
For a smoother experience, set up a proper local development environment. Your development team should always follow best practices when working with Drupal 10 themes or later.
TailwindCSS: Fast and Responsive Layout
TailwindCSS is widely used in custom theme development. It replaces custom CSS with reusable utility classes. In Drupal, Tailwind integrates easily into your development environment and speeds up theme work.
Benefits of Tailwind in Drupal:
- Smaller codebase
- Faster development cycles
- Better responsive layouts
This is ideal when you need flexibility across different screen sizes or want to reduce styling overhead in your custom theme in Drupal.
Theme Starterkit and Custom Theme Customization
Theme Starterkit is a modern method introduced in Drupal 10/11. It allows developers to copy a base theme and fully customise it without changing the core. This ensures stability and easy updates. When working with Drupal's theming system, Starterkit is a reliable choice. You can adjust styles, layouts, and colours, all within your custom theme folder. Use theme_get_setting() in the theme file to make settings visible in templates. This improves the user experience, especially for content managers. Visual changes can be made without involving developers.
Starterkit helps ensure your Drupal theme is flexible and adaptable to your brand. It is designed for performance and ease of maintenance. Ensure that your Drupal theme follows best practices for performance and accessibility.
Content Structure in Drupal Theming
An introduction to Drupal must include understanding content structure. It's essential for clean theming and site usability. When developing D10 or later themes, start with a solid content model.
Taxonomy: Content Categorisation and Filtering
Drupal’s taxonomy system lets to organise content with tags, categories, or topics. This improves filtering, conditional content, and user navigation. It’s a key part of Drupal as a content management platform.
Views: Dynamic Outputs without Code
The Views module allows to build content displays without writing code. Lists, blocks, sliders, and galleries can all be built visually.
Customise how it looks using Drupal’s theming approach. This makes the frontend theme both powerful and user-friendly.
Twig Templates: Customising the Appearance of Materials
Use Twig to build specific layouts for different content types. Filenames like node--article.html.twig live in your theme directory and control how each node appears.
This gives Drupal developers full control over the output of individual pages.
Content Modelling: the Correct Structure of Fields
Before theming, plan content types carefully. Define fields like titles, images, dates, and files. This creates a predictable structure and ensures smooth templating. A well-designed model makes theming faster and the site easier to manage.
SEO, Performance and Accessibility in Drupal Themes
A theme in Drupal is a great design, and it affects speed, search engine optimisation, accessibility. A well-planned theme improves indexing, user experience, and mobile usability.
Semantic HTML Structure
Use semantic tags like header, main, article, and nav. Include ARIA attributes and a clear heading hierarchy. This supports screen readers and improves content indexing. Understanding Drupal’s theme structure helps ensure consistency across templates and better accessibility.
CSS and JS Optimization
Use critical styles at the top of the page and load other styles or scripts later. Combine and minify files to improve loading speed. Use modern formats like WebP for images and lazy loading to boost performance. This creates a theme focused on performance and helps reduce development time. A good starter theme supports these features.
Responsive Design in Drupal Themes
Your Drupal custom theme should adapt to all screen sizes. Use responsive layouts, media queries, and touch-friendly elements. This ensures a consistent experience on phones, tablets, and laptops. Choose a base theme without extra code to keep it clean and fast.
Accessibility
Follow WCAG standards for keyboard navigation, visual focus, and readable contrast. Use Drupal core and contributed modules that support accessibility out of the box. Themes should work well for all users, including those with disabilities.
Monitoring, Testing, and Maintaining Your Drupal Theme
Keep your theme clean by avoiding changes to core files. Use Twig Debugging to see which templates are active. This helps with development and troubleshooting.
Regularly update Drupal core and contributed modules to keep your site secure and compatible.
Use Drupal modules for performance tracking and accessibility audits. Run tests to ensure everything works as expected.
Use A/B testing to see which design changes improve user engagement. Make sure the name of your theme matches your folder and follows Drupal standards.
Why choose Drupfan for Developing a Custom Theme
Drupfan specialises in custom Drupal themes with a strong focus on performance, security, and visual consistency. Each custom Drupal theme provides a seamless user experience across different devices and platforms.
The team follows best practices, using a stack influenced by Swiftorial and Droptica. This includes stable frontend tools and a modern DevOps approach. All updates are tested in a staging environment to ensure safe deployment.
Drupfan builds accessibility-ready themes that follow WCAG 2.1. These make your site more inclusive and aligned with accessibility standards.
Expertise covers Drupal 8, 9, 10, and supports Drupal 11. Whether adapting an existing design or starting from scratch, each theme aligns with your brand goals. A Drupal theme is essential to delivering quality content presentation and site performance.
For developers who want to explore the world of Drupal, this approach helps you get started with confidence. Whether building from a base or extending a theme without altering its core, Drupfan provides a solid foundation.
Drupfan also engages with Drupal community events and applies insights to enhance future projects.
Drupal Theme Development FAQ
❓ What versions of Drupal are supported for theme development?
Themes are built for Drupal 9, 10 and Drupal 11. Drupal 11 offers new tools and flexibility, making it easier to build themes that scale.
❓ What is the difference between a custom theme and a basic theme?
A custom Drupal theme provides full design control and flexibility. Basic themes are often minimal and suited for general use. Custom themes are ideal when branding, performance, and accessibility are priorities.
❓ How is a theme updated after release?
Updates include core, module, and framework changes. Testing happens in a staging environment to avoid disruptions. This ensures themes remain secure and compatible.
❓ How is the theme responsive on mobile devices ensured?
Using a mobile-first approach and frameworks like TailwindCSS, each theme works across different screen sizes. Responsive layouts are tested thoroughly before release.
❓ Can the theme be integrated with Bootstrap, Tailwind, or other CSS frameworks?
Yes. Drupfan supports integration with both Bootstrap 5 and TailwindCSS. These tools are available for free and empower developers to create modern, flexible interfaces.
❓ How are theme settings implemented for customisation?
Settings are added to the theme settings file. Drupal allows administrators to manage colours, logos, and layouts directly from the admin UI.
❓ Is the theme multilingual?
Yes. Multilingual support includes translations, right-to-left layout, and localisation. This is critical for global content strategy.
❓ What are the options for optimising theme performance?
Performance strategies include lazy image loading, script minification, CSS optimisation, and layout checks using Core Web Vitals.
❓ How do I check an accessibility theme?
Tools like Lighthouse, axe, and WCAG checklists are used. These help ensure the theme meets accessibility standards for A and AA levels.
❓ What are the ways to debug templates in Drupal?
Twig debug, Kint, Devel, and the Theme Debug module help track template behavior. These tools are part of a comprehensive guide to effective Drupal theming.
❓ Is it possible to add a dark theme?
Yes. A dark version can be added with a theme switcher or through system settings.
❓ What does the theme development process look like?
The process includes requirements gathering, prototyping, frontend development, Drupal integration, testing, and release. This method ensures that each custom Drupal theme provides both performance and reliability.
❓ How to implement animation in a Drupal theme?
Animations can be added using CSS, JavaScript, or Tailwind. These are always tested for both performance and accessibility.
❓ What is Starterkit in Drupal 10 and 11?
Starterkit is a method that Drupal 10 offers for creating custom themes. It allows developers to copy a base theme and customise it freely. This avoids modifying core themes directly, making maintenance easier.
❓ Is it possible to order only the adaptation of an existing design to a Drupal theme?
Yes. Drupfan can adapt Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD designs into a working theme. This transformation keeps the original style intact.
❓ What happens to unused themes?
Uninstalled themes remain accessible in the uninstalled themes section. They can be reused or updated when needed.